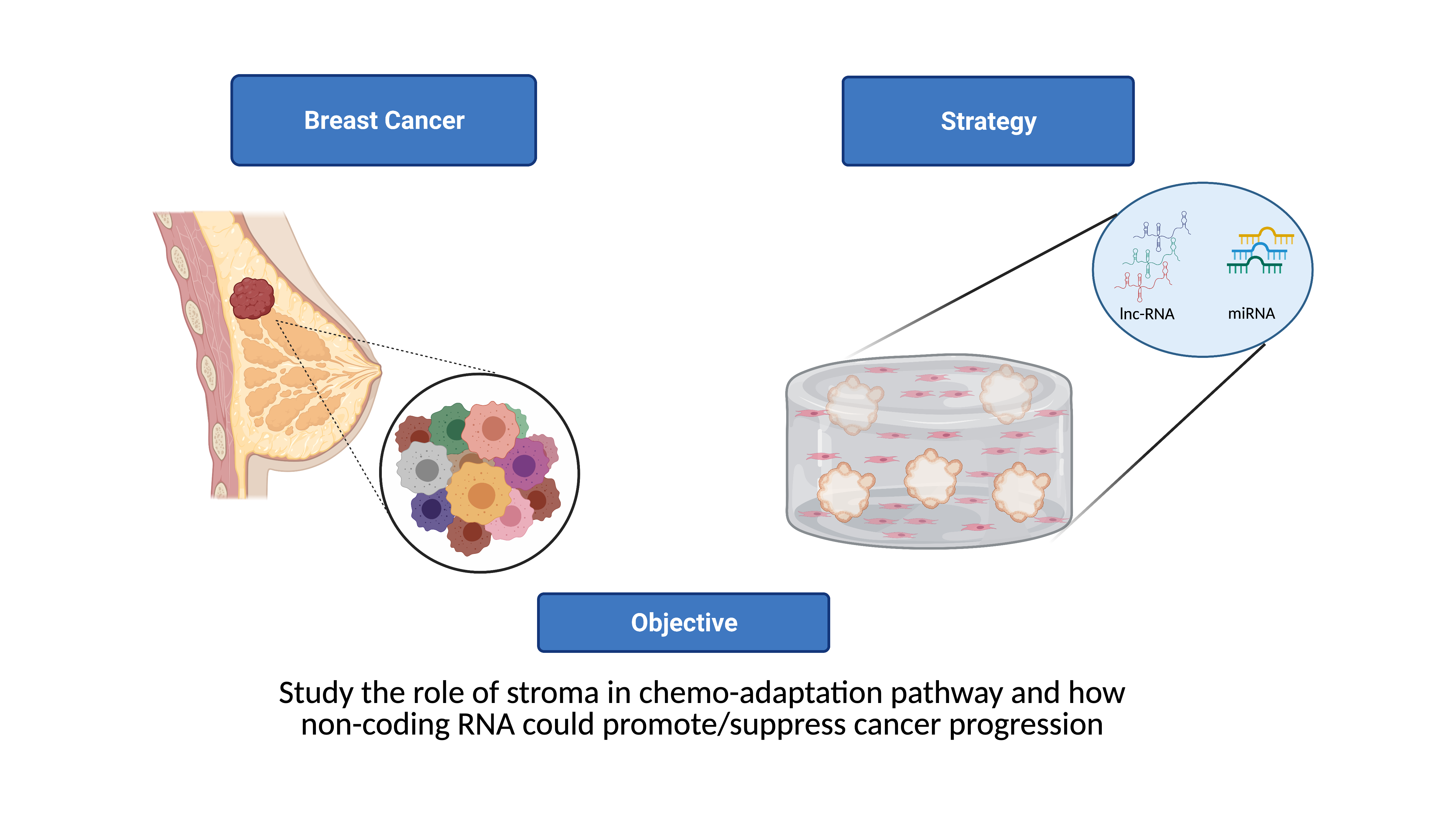
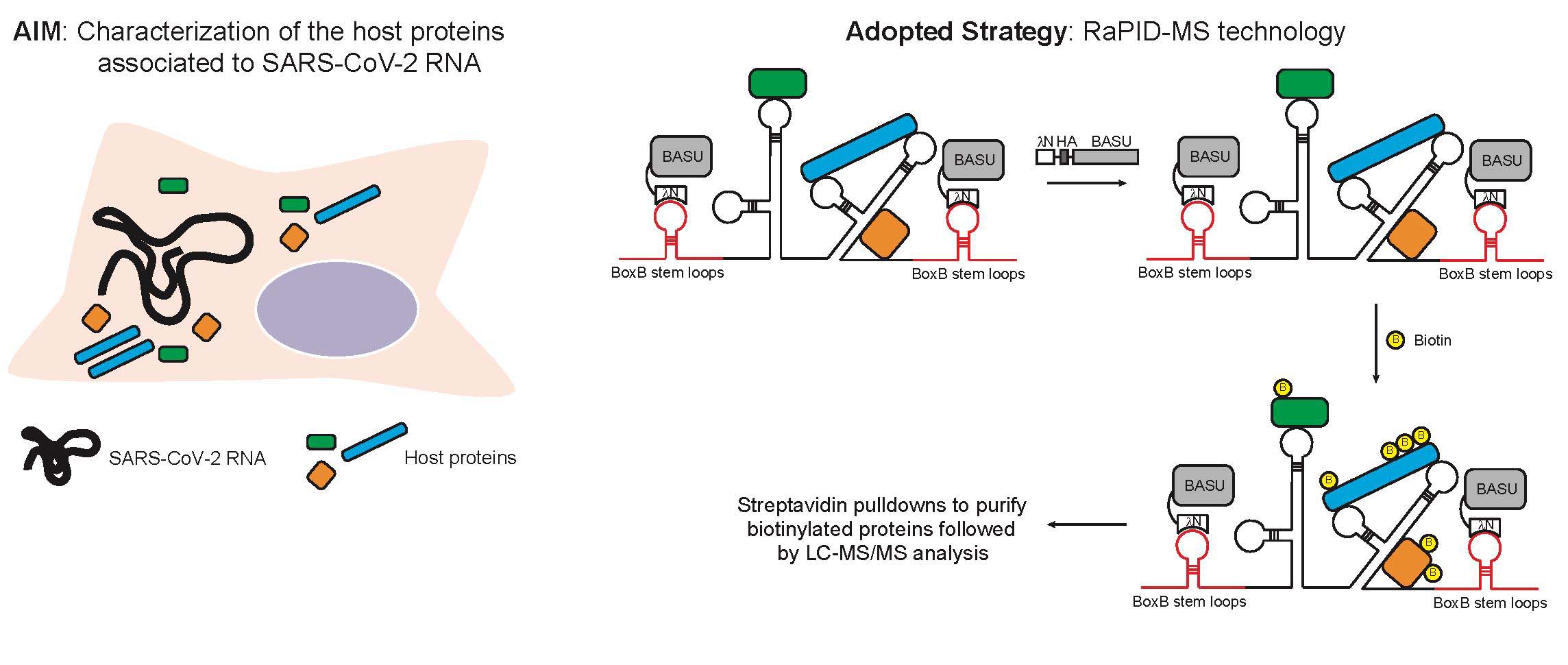
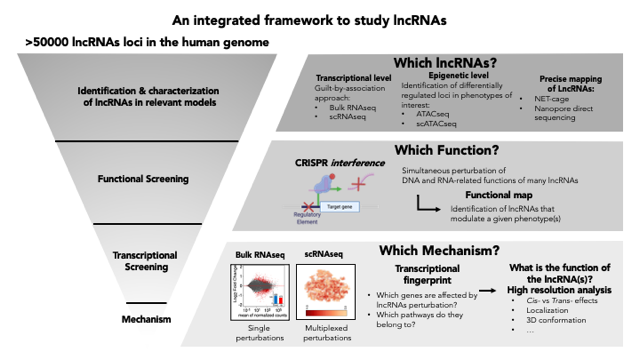
-
Simeone I, Rubolino C, Noviello T, Farinello D, Cerulo L, Marzi MJ, Nicassio F. Prediction and pan-cancer analysis of mammalian transcripts involved in target directed miRNA degradation Nucleic Acids Res. 2022
-
Bido S, Muggeo S, Massimino L, Marzi MJ, Giannelli SG, Melacini E, Nannoni M, Gambarè D, Bellini E, Ordazzo G, Rossi G, Maffezzini C, Iannelli A, Luoni M, Bacigaluppi M, Gregori S, Nicassio F, Broccoli V. Microglia-specific overexpression of α-synuclein leads to severe dopaminergic neurodegeneration by phagocytic exhaustion and oxidative toxicity. Nat Commun. 2021
-
Tordonato C, Marzi MJ, Giangreco G, Freddi S, Bonetti P, Tosoni D, Di Fiore PP, Nicassio F miR-146 connects stem cell identity with metabolism and pharmacological resistance in breast cancer J Cell Biol. 2021
-
Spadotto V, Giambruno R, Massignani E, Mihailovich M, Maniaci M, Patuzzo F, Ghini F, Nicassio F, Bonaldi T. PRMT1-mediated methylation of the microprocessor-associated proteins regulates microRNA biogenesis Nucleic Acids Res. 2020
-
Pons-Espinal M, Gasperini C, Marzi MJ, Braccia C, Armirotti A, Pötzsch A, Walker TL, Fabel K, Nicassio F, Kempermann G, De Pietri Tonelli D. MiR-135a-5p Is Critical for Exercise-Induced Adult Neurogenesis Stem Cell Reports. 2019
-
Rossi M, Bucci G, Rizzotto D, Bordo D, Marzi MJ, Puppo M, Flinois A, Spadaro D, Citi S, Emionite L, Cilli M, Nicassio F, Inga A, Briata P, Gherzi R. LncRNA EPR controls epithelial proliferation by coordinating Cdkn1a transcription and mRNA decay response to TGF-β Nat Commun. 2019
-
Panebianco F, Climent M, Malvindi MA, Pompa PP, Bonetti P, Nicassio F Delivery of biologically active miR-34a in normal and cancer mammary epithelial cells by synthetic nanoparticles Nanomedicine 2019
-
Santoro A, Vlachou T, Luzi L, Melloni G, Mazzarella L, D'Elia E, Aobuli X, Pasi CE, Reavie L, Bonetti P, Punzi S, Casoli L, Sabò A, Moroni MC, Dellino GI, Amati B, Nicassio F, Lanfrancone L, Pelicci PG. p53 Loss in Breast Cancer Leads to Myc Activation, Increased Cell Plasticity, and Expression of a Mitotic Signature with Prognostic Value Cell Rep. 2019
-
Bonetti P, Climent M, Panebianco F, Tordonato C, Santoro A, Marzi MJ, Pelicci PG, Ventura A, Nicassio F. Dual role for miR-34a in the control of early progenitor proliferation and commitment in the mammary gland and in breast cancer Oncogene 2019
-
Ghini F, Rubolino C, Climent M, Simeone I, Marzi MJ, Nicassio F. Endogenous Transcripts control miRNA levels and activity in mammalian cells by target-directed miRNA degradation Nature Communications 2018
-
Culurgioni S, Mari S, Bonetti P, Gallini S, Bonetto G, Brennich M, Round A, Nicassio F, Mapelli M. Insc:LGN tetramers promote asymmetric divisions of mammary stem cells Nature Communications 2018
-
Pons-Espinal M, de Luca E, Marzi MJ, Beckervordersandforth R, Armirotti A, Nicassio F, Fabel K, Kempermann G, De Pietri Tonelli D. Synergic Functions of miRNAs Determine Neuronal Fate of Adult Neural Stem Cells Stem Cell Reports 2017
-
Marinaro F, Marzi MJ, Hoffmann N, Amin H, Pelizzoli R, Niola F, Nicassio F, De Pietri Tonelli D. MicroRNA-independent functions of DGCR8 are essential for neocortical development and TBR1 expression EMBO Reports 2017
-
Marzi MJ, Montani F, Carletti RM, Dezi F, Dama E, Bonizzi G, Sandri MT, Rampinelli C, Bellomi M, Maisonneuve P, Spaggiari L, Veronesi G, Bianchi F, Di Fiore PP, Nicassio F. Optimization and Standardization of Circulating MicroRNA Detection for Clinical Application: The miR-Test Case Clinical Chemistry 2016
-
Marzi MJ, Ghini F, Cerruti B, de Pretis S, Bonetti P, Giacomelli C, Gorski MM, Kress T, Pelizzola M, Muller H, Amati B, Nicassio F. Degradation dynamics of microRNAs revealed by a novel pulsechase approach Genome Research 2016